2020全新 最火Vue面试题训练营
1.Vue.use是干什么的?原理是什么?
核心答案:
Vue.use是用来使用插件的,我们可以在插件中扩展全局组件、指令、原型方法等。
Vue.use = function (plugin: Function | Object) {
// 插件不能重复的加载
const installedPlugins = (this._installedPlugins || (this._installedPlugins = []))
if (installedPlugins.indexOf(plugin) > -1) {
return this
}
// additional parameters
const args = toArray(arguments, 1)
args.unshift(this) // install方法的第一个参数是Vue的构造函数,其他参数是Vue.use中除了第一个参数的其他参数
if (typeof plugin.install === 'function') { // 调用插件的install方法
plugin.install.apply(plugin, args) Vue.install = function(Vue,args){}
} else if (typeof plugin === 'function') { // 插件本身是一个函数,直接让函数执行
plugin.apply(null, args)
}
installedPlugins.push(plugin) // 缓存插件
return this
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
源码位置:
src/core/global-api/use.js:5
2.vue-router有几种钩子函数?具体是什么及执行流程是怎样的?
核心答案:
路由钩子的执行流程, 钩子函数种类有:全局守卫、路由守卫、组件守卫
完整的导航解析流程:
- ①导航被触发。
- ②在失活的组件里调用
beforeRouteLeave守卫。 - ③调用全局的
beforeEach守卫。 - ④在重用的组件里调用
beforeRouteUpdate守卫 (2.2+)。 - ⑤在路由配置里调用
beforeEnter。 - ⑥解析异步路由组件。
- ⑦在被激活的组件里调用
beforeRouteEnter。 - ⑧调用全局的
beforeResolve守卫 (2.5+)。 - ⑨导航被确认。
- ⑩调用全局的
afterEach钩子。 - ⑪触发 DOM 更新。
- ⑫调用
beforeRouteEnter守卫中传给 next 的回调函数,创建好的组件实例会作为回调函数的参数传入。
3.vue-router两种模式的区别?
核心答案:
hash模式、history模式
- hash模式:
hash+hashChange兼容性好但是不美观 - history模式 :
historyApi+popState虽然美观,但是刷新会出现404需要后端进行配置
4.函数式组件的优势及原理
核心答案:
函数式组件的特性,无状态、无生命周期、无this
if (isTrue(Ctor.options.functional)) { // 带有functional的属性的就是函数式组件
return createFunctionalComponent(Ctor, propsData, data, context, children)
}
const listeners = data.on
data.on = data.nativeOn
installComponentHooks(data) // 安装组件相关钩子 (函数式组件没有调用此方法,从而性能高于普通组件)
2
3
4
5
6
源码位置: src/core/vdom/create-component.js:164、src/core/vdom/create-functional-component.js:5
5.v-if与v-for的优先级
核心答案:
v-for和v-if不要在同一个标签中使用,因为解析时先解析v-for在解析v-if。如果遇到需要同时使用时可以考虑写成计算属性的方式。
if (el.staticRoot && !el.staticProcessed) {
return genStatic(el, state)
} else if (el.once && !el.onceProcessed) {
return genOnce(el, state)
} else if (el.for && !el.forProcessed) {
return genFor(el, state) // v-for
} else if (el.if && !el.ifProcessed) {
return genIf(el, state) // v-if
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
源码位置:
src/compiler/codegen/index.js:55
6.组件中写name选项又哪些好处及作用?
核心答案:
- 可以通过名字找到对应的组件 (递归组件)
- 可用通过name属性实现缓存功能 (keep-alive)
- 可以通过name来识别组件 (跨级组件通信时非常重要)
Vue.extend = function(){
if (name) {
Sub.options.components[name] = Sub
}
}
2
3
4
5
源码位置:
src/core/vdom/create-element.js:111
7.Vue事件修饰符有哪些?其实现原理是什么?
核心答案:
事件修饰符有:.capture、.once、.passive 、.stop、.self、.prevent、
//①生成ast时处理
export function addHandler (
el: ASTElement,
name: string,
value: string,
modifiers: ?ASTModifiers,
important?: boolean,
warn?: ?Function,
range?: Range,
dynamic?: boolean
) {
modifiers = modifiers || emptyObject
// check capture modifier
if (modifiers.capture) { // 如果是capture 加!
delete modifiers.capture
name = prependModifierMarker('!', name, dynamic)
}
if (modifiers.once) { // 如果是once加~
delete modifiers.once
name = prependModifierMarker('~', name, dynamic)
}
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (modifiers.passive) { // 如果是passive 加&
delete modifiers.passive
name = prependModifierMarker('&', name, dynamic)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
源码位置:
src/compiler/helpers.js:69
//②codegen时处理
const genGuard = condition => `if(${condition})return null;`
const modifierCode: { [key: string]: string } = {
stop: '$event.stopPropagation();', // 增加阻止默认事件
prevent: '$event.preventDefault();', // 阻止默认行为
self: genGuard(`$event.target !== $event.currentTarget`), // 点击是否是自己
}
for (const key in handler.modifiers) {
if (modifierCode[key]) {
genModifierCode += modifierCode[key]
}
if (genModifierCode) {
code += genModifierCode
}
const handlerCode = isMethodPath
? `return ${handler.value}($event)`
: isFunctionExpression
? `return (${handler.value})($event)`
: isFunctionInvocation
? `return ${handler.value}`
: handler.value
return `function($event){${code}${handlerCode}}`
}
//③处理on事件
for (name in on) {
def = cur = on[name]
old = oldOn[name]
event = normalizeEvent(name) // 处理& ! ~
if (isTrue(event.once)) {
cur = on[name] = createOnceHandler(event.name, cur, event.capture)
}
add(event.name, cur, event.capture, event.passive, event.params) // 调用addEventListener绑定事件
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
源码位置:
src/compiler/codegen/events.js:42
源码位置:
src/core/vdom/helpers/update-listeners.js:65
8.Vue.directive源码实现?
核心答案:
把定义的内容进行格式化挂载到Vue.options属性上
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => {
Vue[type] = function (
id: string,
definition: Function | Object
): Function | Object | void {
if (!definition) {
return this.options[type + 's'][id]
} else { // 如果是指令 将指令的定义包装成对象
if (type === 'directive' && typeof definition === 'function') {
definition = { bind: definition, update: definition }
}
this.options[type + 's'][id] = definition // 将指令的定义绑定在Vue.options上
return definition
}
}
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
源码位置:
core/global-api/assets.js
9.如何理解自定义指令?
核心答案:
指令的实现原理,可以从编译原理=>代码生成=>指令钩子实现进行概述
1.在生成
ast语法树时,遇到指令会给当前元素添加directives属性2.通过
genDirectives生成指令代码3.在patch前将指令的钩子提取到
cbs中,在patch过程中调用对应的钩子4.当执行指令对应钩子函数时,调用对应指令定义的方法
export function addDirective (
el: ASTElement,
name: string,
rawName: string,
value: string,
arg: ?string,
isDynamicArg: boolean,
modifiers: ?ASTModifiers,
range?: Range
) {
(el.directives || (el.directives = [])).push(rangeSetItem({ // 给元素添加directives属性
name,
rawName,
value,
arg,
isDynamicArg,
modifiers
}, range))
el.plain = false
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
function genDirectives (el: ASTElement, state: CodegenState): string | void {
const dirs = el.directives
if (!dirs) return
let res = 'directives:['
let hasRuntime = false
let i, l, dir, needRuntime
for (i = 0, l = dirs.length; i < l; i++) {
dir = dirs[i]
needRuntime = true
if (needRuntime) {
hasRuntime = true
// 将指令生成字符串directives:[{name:'def',rawName:'v-def'}]...
res += `{name:"${dir.name}",rawName:"${dir.rawName}"${
dir.value ? `,value:(${dir.value}),expression:${JSON.stringify(dir.value)}` : ''
}${
dir.arg ? `,arg:${dir.isDynamicArg ? dir.arg : `"${dir.arg}"`}` : ''
}${
dir.modifiers ? `,modifiers:${JSON.stringify(dir.modifiers)}` : ''
}},`
}
}
if (hasRuntime) {
return res.slice(0, -1) + ']'
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
const hooks = ['create', 'activate', 'update', 'remove', 'destroy']
const { modules, nodeOps } = backend // // modules包含指令对应的hook
for (i = 0; i < hooks.length; ++i) {
cbs[hooks[i]] = []
for (j = 0; j < modules.length; ++j) {
// 格式化的结果{create:[hook],update:[hook],destroy:[hook]}
if (isDef(modules[j][hooks[i]])) {
cbs[hooks[i]].push(modules[j][hooks[i]])
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
export default { // 无论更新创建销毁调用的都是 updateDirectives方法
create: updateDirectives,
update: updateDirectives,
destroy: function unbindDirectives (vnode: VNodeWithData) {
updateDirectives(vnode, emptyNode)
}
}
function updateDirectives (oldVnode: VNodeWithData, vnode: VNodeWithData) {
if (oldVnode.data.directives || vnode.data.directives) { // 创建更新都调用此方法
_update(oldVnode, vnode) // 指令的核心方法
}
}
function _update (oldVnode, vnode) {
const isCreate = oldVnode === emptyNode
const isDestroy = vnode === emptyNode
// 获取指令名称
const oldDirs = normalizeDirectives(oldVnode.data.directives, oldVnode.context)
const newDirs = normalizeDirectives(vnode.data.directives, vnode.context)
const dirsWithInsert = []
const dirsWithPostpatch = []
let key, oldDir, dir
for (key in newDirs) {
oldDir = oldDirs[key]
dir = newDirs[key]
if (!oldDir) { // 没有旧的 说明是绑定 调用bind钩子
// new directive, bind
callHook(dir, 'bind', vnode, oldVnode)
if (dir.def && dir.def.inserted) {
dirsWithInsert.push(dir)
}
} else { // 存在指令则是更新操作
// existing directive, update
dir.oldValue = oldDir.value
dir.oldArg = oldDir.arg
callHook(dir, 'update', vnode, oldVnode)
if (dir.def && dir.def.componentUpdated) { // 如果有componentUpdated方法
dirsWithPostpatch.push(dir)
}
}
}
if (dirsWithInsert.length) { // 如果有insert钩子
const callInsert = () => { // 生成回调方法
for (let i = 0; i < dirsWithInsert.length; i++) {
callHook(dirsWithInsert[i], 'inserted', vnode, oldVnode)
}
}
if (isCreate) { // 是创建增加insert钩子
mergeVNodeHook(vnode, 'insert', callInsert)
} else {
callInsert()
}
}
if (dirsWithPostpatch.length) { // 如果有componentUpdated在次合并钩子
mergeVNodeHook(vnode, 'postpatch', () => {
for (let i = 0; i < dirsWithPostpatch.length; i++) {
callHook(dirsWithPostpatch[i], 'componentUpdated', vnode, oldVnode)
}
})
}
if (!isCreate) { // 否则就是调用卸载钩子
for (key in oldDirs) {
if (!newDirs[key]) {
// no longer present, unbind
callHook(oldDirs[key], 'unbind', oldVnode, oldVnode, isDestroy)
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
源码位置:
src/compiler/helpers.js:42源码位置:
src/compiler/codegen/index.js:309源码位置:
src/core/vdom/patch:70源码位置:
src/core/vdom/modules/directives:7
10.谈一下你对vuex的个人理解
核心答案:
vuex是专门为vue提供的全局状态管理系统,用于多个组件中数据共享、数据缓存等。(无法持久化、内部核心原理是通过创造一个全局实例 new Vue)
- 衍生的问题
action和mutation的区别 - 核心方法:
replaceState、subscribe、registerModule、namespace(modules)
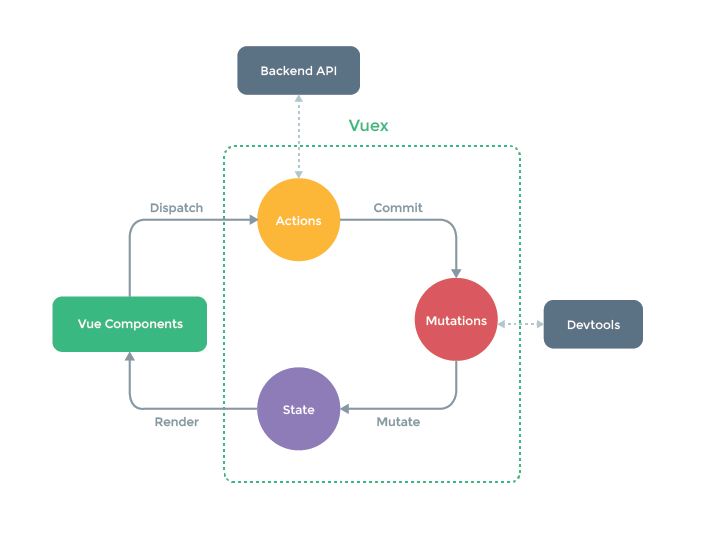
11.Vue中slot是如何实现的?什么时候用它?
核心答案:
普通插槽(模板传入到组件中,数据采用父组件数据)和作用域插槽(在父组件中访问子组件数据)
12.keep-alive平时在哪使用?原理是?
keep-alive主要是缓存,采用的是LRU算法。 最近最久未使用法。

原理地址:
src/core/components/keep-alive.js
13.$refs是如何实现的?
核心答案:
将真实DOM或者组件实例挂载在当前实例的$refs属性上
export function registerRef (vnode: VNodeWithData, isRemoval: ?boolean) {
const key = vnode.data.ref // 获取ref
if (!isDef(key)) return
const vm = vnode.context
const ref = vnode.componentInstance || vnode.elm // 如果是组件则采用实例 否则真是dom
const refs = vm.$refs
if (isRemoval) {
if (Array.isArray(refs[key])) {
remove(refs[key], ref)
} else if (refs[key] === ref) {
refs[key] = undefined
}
} else {
if (vnode.data.refInFor) { // 在v-for中是数组
if (!Array.isArray(refs[key])) {
refs[key] = [ref]
} else if (refs[key].indexOf(ref) < 0) {
// $flow-disable-line
refs[key].push(ref)
}
} else {
refs[key] = ref
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
14.vue中使用了哪些设计模式?
工厂模式 - 传入参数即可创建实例 (
createElement)根据传入的参数不同返回不同的实例
export function _createElement ( context: Component, tag?: string | Class<Component> | Function | Object, data?: VNodeData, children?: any, normalizationType?: number ): VNode | Array<VNode> { // ... if (typeof tag === 'string') { let Ctor ns = (context.$vnode && context.$vnode.ns) || config.getTagNamespace(tag) if (config.isReservedTag(tag)) { vnode = new VNode( config.parsePlatformTagName(tag), data, children, undefined, undefined, context ) } else if ((!data || !data.pre) && isDef(Ctor = resolveAsset(context.$options, 'components', tag))) { vnode = createComponent(Ctor, data, context, children, tag) } else { vnode = new VNode( tag, data, children, undefined, undefined, context ) } } else { vnode = createComponent(tag, data, context, children) } // .... }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29单例模式
单例模式就是整个程序有且仅有一个实例。
export function install (_Vue) { if (Vue && _Vue === Vue) { if (__DEV__) { console.error( '[vuex] already installed. Vue.use(Vuex) should be called only once.' ) } return } Vue = _Vue applyMixin(Vue) }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12发布-订阅模式
订阅者把自己想订阅的事件注册到调度中心,当该事件触发时候,发布者发布该事件到调度中心,由调度中心统一调度订阅者注册到调度中心的处理代码。
Vue.prototype.$on = function (event: string | Array<string>, fn: Function): Component { const vm: Component = this if (Array.isArray(event)) { for (let i = 0, l = event.length; i < l; i++) { vm.$on(event[i], fn) } } else { (vm._events[event] || (vm._events[event] = [])).push(fn) if (hookRE.test(event)) { vm._hasHookEvent = true } } return vm } Vue.prototype.$emit = function (event: string): Component { const vm: Component = this let cbs = vm._events[event] if (cbs) { cbs = cbs.length > 1 ? toArray(cbs) : cbs const args = toArray(arguments, 1) const info = `event handler for "${event}"` for (let i = 0, l = cbs.length; i < l; i++) { invokeWithErrorHandling(cbs[i], vm, args, vm, info) } } return vm }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27观察者模式 :
watcher&dep的关系代理模式 (防抖和节流) => 返回替代 (例如:
Vue3中的proxy)代理模式给某一个对象提供一个代理对象,并由代理对象控制对原对象的引用。
装饰模式: @装饰器的用法
中介者模式 =>
vuex中介者是一个行为设计模式,通过提供一个统一的接口让系统的不同部分进行通信。
策略模式 策略模式指对象有某个行为,但是在不同的场景中,该行为有不同的实现方案。
function mergeField (key) { const strat = strats[key] || defaultStrat options[key] = strat(parent[key], child[key], vm, key) }1
2
3
4外观模式、适配器模式、迭代器模式、模板方法模式 .....
15.谈谈Vue3和Vue2的区别?
- 对
TypeScript支持不友好(所有属性都放在了this对象上,难以推倒组件的数据类型) - 大量的
API挂载在Vue对象的原型上,难以实现TreeShaking。 - 架构层面对跨平台
dom渲染开发支持不友好 CompositionAPI。受ReactHook启发- 对虚拟DOM进行了重写、对模板的编译进行了优化操作...